4-Hydroxy-D-phenylglycine (CAS No.: 22818-40-2) is a fine pharmaceutical chemical that plays an essential role in the synthesis of several vital β-lactam antibiotics, as well as functioning as an antimicrobial agent in other industries. With its unique stereochemistry and reactive functional groups, 4-HDPG serves as a key building block in the production of penicillins and cephalosporins. In this blog post, Viablife, a high purity fine pharmaceutical chemicals manufacturer, will share the effects of key intermediate 4-Hydroxy-D-Phenylglycine.
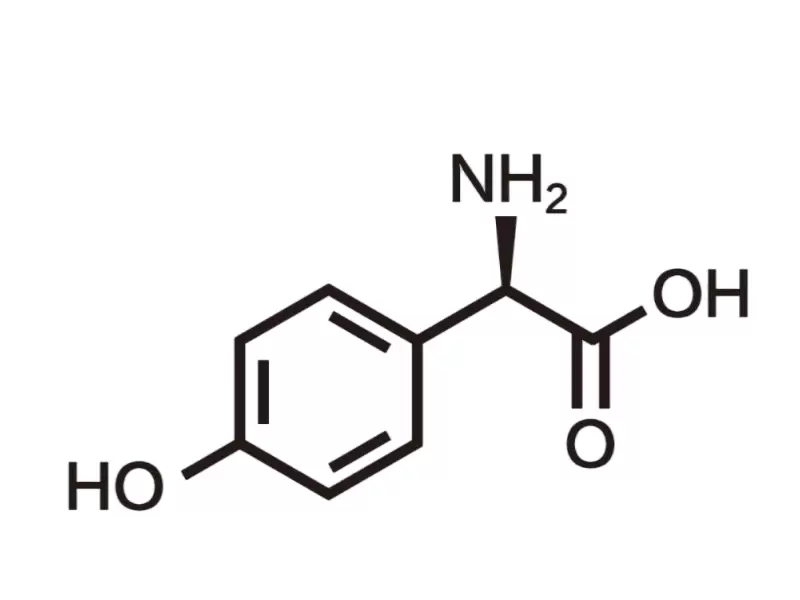
Effects of Fine Pharmaceutical Chemical 4-Hydroxy-D-Phenylglycine
1. Key Intermediate for Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin is one of the most widely used antibiotics globally, known for its broad-spectrum activity and high oral bioavailability. 4-Hydroxy-D-phenylglycine serves as a critical intermediate in the semi-synthetic production of amoxicillin.
In the biosynthetic pathway, 4-HDPG contributes the side chain that is attached to the core β-lactam ring structure derived from 6-aminopenicillanic acid (6-APA). The presence of the hydroxyl group in the phenylglycine moiety significantly enhances the hydrophilic nature of amoxicillin, allowing it to exhibit improved solubility and better absorption in the gastrointestinal tract compared to earlier antibiotics like ampicillin.
The stereochemical purity of 4-HDPG is essential, as it directly affects the pharmacological efficacy and metabolic stability of the final product. The D-isomer, in particular, ensures proper binding affinity to bacterial penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs), leading to effective inhibition of bacterial cell wall synthesis.
2. Crucial Intermediate in β-Lactam Synthesis
Beyond amoxicillin, 4-Hydroxy-D-phenylglycine is used as a universal side-chain donor in the synthesis of a range of β-lactam antibiotics. Its chiral center and functional groups make it amenable to nucleophilic substitution reactions required in the attachment to various antibiotic scaffolds.
In industrial synthesis, the compound is introduced during the acylation step, where it reacts with the β-lactam core under controlled conditions to produce high-yield intermediates. This step is crucial for maintaining batch-to-batch consistency, ensuring product quality, and reducing manufacturing costs.
Because of its reliable chemical reactivity and compatibility with different reaction conditions, 4-HDPG helps streamline the semi-synthetic routes to many life-saving drugs, reducing environmental impact compared to fully synthetic approaches.
3. Key Intermediate for Cefoperazone
Cefoperazone is a third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic, recognized for its activity against gram-negative bacteria and its resistance to β-lactamase degradation. In its production, 4-Hydroxy-D-phenylglycine again plays a pivotal role as an intermediate.
This compound is particularly valued for contributing to the side chain structure that provides increased spectrum of activity and pharmacokinetic properties in cefoperazone. It influences the drug' s tissue penetration and half-life, improving its clinical performance.
Given the increasing threat of antibiotic resistance, intermediates like 4-HDPG enable the creation of next-generation antibiotics with enhanced properties. Their use ensures that modifications at the molecular level can translate to real-world benefits, such as improved efficacy in hospital-acquired infections and immunocompromised patients.
4. Vital Intermediate in the Synthesis of Cefprozil
Cefprozil is another cephalosporin antibiotic where 4-Hydroxy-D-phenylglycine plays a vital synthetic role. As a second-generation cephalosporin, cefprozil exhibits strong activity against both gram-positive and gram-negative organisms, making it useful in the improvement of respiratory and skin infections.
In cefprozil synthesis, 4-HDPG serves as the chiral amino acid side chain, significantly influencing the drug' s stereoselectivity and potency. Proper enantiomeric purity of 4-HDPG ensures that the resulting cefprozil is both pharmacologically active and free of unwanted side effects that may arise from stereoisomeric impurities.
In manufacturing, the chemical provides reaction flexibility, allowing pharmaceutical chemists to optimize yields while ensuring high standards of regulatory compliance and quality assurance.
5. Antimicrobial Properties as a Preservative
Beyond pharmaceutical synthesis, 4-Hydroxy-D-phenylglycine finds utility in the preservation of consumer products, including food, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals. Its antimicrobial properties make it effective in preventing microbial spoilage, thereby extending product shelf life and ensuring user safety.
Due to its biological origin and relative biocompatibility, 4-HDPG is considered a safe and effective preservative. It inhibits the growth of a wide range of microbes, including molds, yeasts, and bacteria, without significantly altering the product's sensory or physical properties.
In cosmetic formulations, it helps maintain product integrity under various environmental conditions. In food processing, it contributes to microbial safety without requiring synthetic preservatives that may have adverse health concerns. The chemical' s mild profile and wide-spectrum activity make it a preferred choice in natural and "clean label” product formulations.
Conclusion
4-Hydroxy-D-phenylglycine is a versatile and indispensable fine chemical in the pharmaceutical industry and beyond. As a key intermediate in the production of essential antibiotics like amoxicillin, cefoperazone, and cefprozil, it plays a critical role in fighting bacterial infections. Its utility extends into consumer products, where it provides antimicrobial protection as a preservative.
The ongoing demand for effective antibiotics and safe preservatives ensures that 4-HDPG will remain a cornerstone chemical in both drug development and product preservation. As manufacturing technologies evolve, sustainable and cost-effective production of 4-HDPG will further enhance its applications, contributing to both public health and industrial innovation.





 Leave a Message
Leave a Message