Basic information of Ceramide Powder for sale:
High purity Ceramide powder for sale is the main lipid component of the lamellar lamellae present in the intercellular spaces of the stratum corneum. These lamellar lamellae are supposed to provide the barrier properties of the epidermis. The intercellular lipid domain is composed of approximately 45-50% ceramide, 25% cholesterol, 15% free fatty acids, and 2% phytosphingosine.
The discovery of a lipid in the nervous tissue of the brain dates back to 1884, when Johann Thudichum identified it in his publication A Treatise on the Chemical Constitution of the Brain. Due to its complex and enigmatic biological function, the lipid was named "sphingolipid," derived from "Sphingo-," referencing the Sphinx of ancient Egyptian mythology.
Sphingolipids were later classified into three main types: sphingomyelins, glycosphingolipids, and ceramides.
Ceramides are structurally heterogeneous and complex sphingolipids that differ in chain length, type and degree of hydroxylation, and saturation level. They are formed through the covalent condensation of sphingosine and long-chain fatty acids with 12 to 30 carbon atoms. Different combinations of three sphingosine and four fatty acids are connected through amide to form different ceramides in the stratum corneum, mainly twelve types. Among these, Ceramide NP is the most abundant and functionally significant.
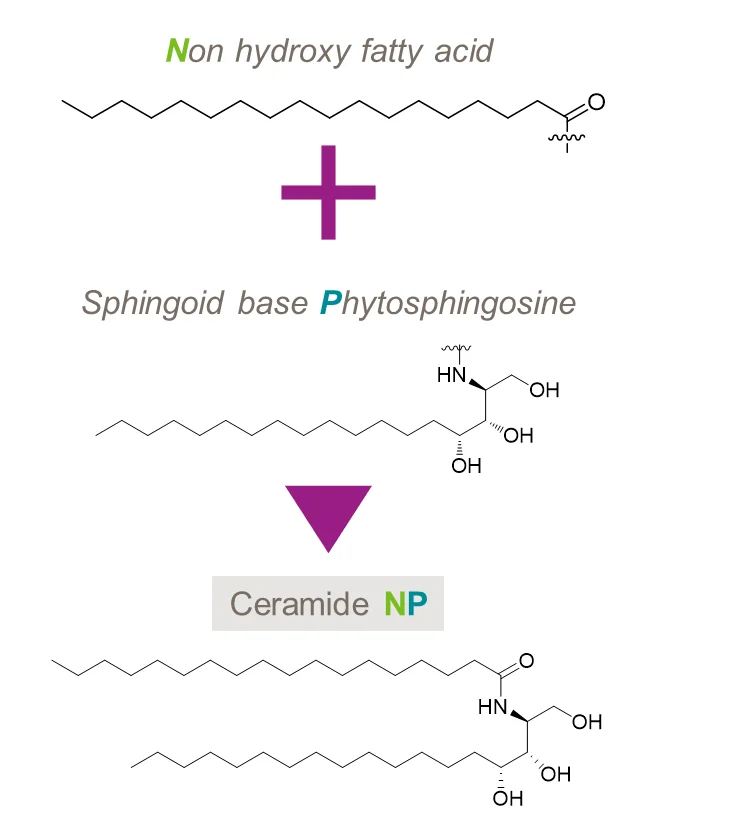
1.Natural extraction
In 1884, German physician Thudichum discovered the presence of sphingosine in the human brain, and later discovered that it is also distributed in animals, plants and some microorganisms. In 1906, Winterstein reported the presence of galactosylceramide in wheat. In the past, ceramides were mainly extracted from animal brains, but since the outbreak of "mad cow disease" in 1986, animal-derived ceramide products have been replaced by plant-based ceramides.
Naturally derived ceramides are derived from animal and plant sources. Extracts of animal origin are almost never used in skin care products due to the risk of immunogenicity and pathogenicity. Plant extraction methods are limited by plant growth cycles and seasons, and have low yields.
2.Chemical synthesis
The main chemical synthesis is ceramide, which has a similar structure and function to ceramide and can be used in cosmetics.
3.Microbial fermentation
Microbial fermentation is a commonly used method for preparing ceramide in recent years. It is fermented under a certain environment to obtain tetraacetyl phytosphingosine (TAPS), which is then deacetylated to obtain phytosphingosine, and fatty acids are added to synthesize ceramide and other substances. Allergenic ingredients will also be decomposed during the fermentation process, so it has high stability and safety. The purity of the ceramide obtained from the fermentation is as high as over 95%. Bio-fermented ceramide has the same structure as ceramide in human skin, is easier to be absorbed by the body, and is more suitable for sensitive skin.
Effects of Ceramide Powder for Skin:
1.Moisturizing
As the most abundant component of intercellular lipids, ceramide plays a very important role in the skin. First of all, ceramide has a large number of hydrophilic groups, which has a strong affinity for water, can prevent the loss of water and electrolytes, and has an endogenous moisturizing effect.
2.Delaying skin aging
As age increases, the ceramides and moisture present in the stratum corneum of human skin gradually decrease. Timely replenishment of ceramides can help delay skin aging and keep skin young.
3.Repairing skin barrier
According to the "brick wall theory" of the skin's natural barrier, keratinocytes are equivalent to bricks, and sebum membranes and intercellular lipids (ceramides, fatty acids, cholesterol, etc.) are cement, they stack up to form a "wall", thus forming a skin's natural protective barrier, ceramides are an important component in the brickwork structure and play a role in protecting the skin barrier. At the same time, ceramide and cell epidermal proteins can be connected through ester bonds to bond cells, preventing dryness, scaling, and scaly skin.

4.Reducing atopic dermatitis
For patients with atopic dermatitis, or patients with dermatitis caused by exposure to surfactants or organic solvents, ceramide NPs in the skin will be rapidly lost. The pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis is unclear and may be related to genetic factors, immune factors, skin barrier dysfunction, mental factors, lifestyle habits and environmental factors. Research shows that the primary mechanism of atopic dermatitis may be skin barrier dysfunction, especially the reduction of ceramide NP content in lipids, which is one of the main reasons for the impairment of skin barrier function. Timely replenishment of ceramides in the skin, especially ceramide NP, has important clinical significance in guiding medication for patients with atopic dermatitis.
5.Soothing skin
Ceramide maintains skin moisture by forming a network structure in the stratum corneum, improving dry skin, reducing scaling, and relieving redness, itching and other discomforts.
Advantages of Viable Ceramide NP Powder for sale:
1.Pure appearance and color
Viable Ceramide NP for skin is pure white powder, ensuring premium quality and consistency.
2.Higher purity
Viable Ceramide NP white powder for sale is produced by biosynthesis process, with higher purity and minimal impurities.
3.Uniform particle size
The particle size of Viable white powder Ceramide NP in skincare is strictly controlled, resulting in a more uniform and consistent product.
4.Formula guidance
As a highly crystalline substance, Ceramide NP for skin is low solubility in water and oil phases, poor dispersibility, and easy crystallization and precipitation, which limits its application in cosmetics. Ceramide manufacturer and Ceramide np supplier Viablife offers professional formulation guidance and tailored recommendations to optimize the application of Viable Ceramide NP powder for sale.
As a high quality ceramide np powder supplier, Viablife are committed to supplying all kinds of cosmetic raw materials!








 Leave a Message
Leave a Message